The year 2024 was marked by seismic shifts across global markets, driven by pivotal events that reshaped the economic and financial landscape.
From Japan’s historic decision to end its negative interest rate policy to the dramatic Wall Street crash in August, and the Federal Reserve’s first rate cut since the pandemic recovery, each event carried profound implications for traders and investors. Adding to the year’s significance was Donald Trump’s return to the presidency, which sparked optimism in some sectors while introducing new uncertainties.
This article delves into these defining moments, unpacking their market impact and what they signal for the future of trading and investment strategies. We will explore some of the most pivotal events of 2024, offering insights to help shape your trading strategies in the years to come.
Japan Ends Negative Rates: Historic March Interest Rate Hike
On 19 March 2024, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) made a historic move by implementing its first interest rate hike in 17 years, raising the benchmark rate from negative territory to a range of 0% to 0.1% [1]. This decision marked the end of Japan’s era of negative interest rates, a policy introduced in 2016 to combat deflation and stimulate economic activity. The rate hike reflected a significant shift in Japan’s monetary policy, driven by improving economic indicators, such as steady inflation and wage growth, which signaled progress toward achieving the BOJ’s 2% inflation target.
The policy change had profound implications for global markets, especially the forex market. The yen strengthened sharply as traders unwound popular yen-funded carry trades—a strategy involving borrowing in low-yielding yen to invest in higher-yielding assets abroad. This sudden appreciation of the yen not only disrupted forex markets but also triggered a broader sell-off in risk assets, including equities, as investors adjusted to rising borrowing costs and diminishing returns.
On 31 July 2024, Japan’s central bank implemented a further 0.25% interest rate hike, which created significant market turbulence by August 2024 [2]. The intensification of carry trade unwinding contributed to sharp declines in global stock indices, drawing comparisons to historic market crashes. The BOJ’s policy shift highlighted the delicate balance central banks must maintain when responding to changing economic conditions, demonstrating the far-reaching impact of monetary policy decisions on global financial markets.
August Market Meltdown: The Wall Street Crash of 2024 [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
The impact of Japan’s monetary policy shift reached its peak on 5 August 2024, as global markets experienced a dramatic downturn. Triggered by Japan’s unexpected interest rate hike and growing concerns about a slowing US economy, major indices plummeted across the board. The yen’s sharp appreciation and the unwinding of the yen carry trade further destabilised markets, intensifying investor anxiety on a global scale.
The upheaval drew comparisons to the infamous “Black Monday” of October 1987, when the S&P 500 and Nasdaq suffered single-day losses of 20% and 11.5%, respectively. This time, Japan was at the centre of the crisis, as the Tokyo Nikkei 225 index recorded one of its steepest declines, closing over 12% lower in a single day. In Korea, the Kospi index also experienced significant turmoil, plunging nearly 9% and triggering a rare 20-minute trading halt—the first in four years—after an unprecedented 8% drop within a minute.
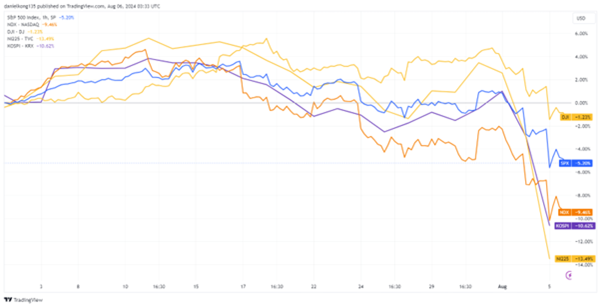
In the United States, the fallout was less severe but still significant. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) fell 2.6%, while the S&P 500 and Nasdaq Composite declined by 3%. These losses extended a difficult week for US markets, with the Nasdaq down more than 13% from its record high in July.
Tech giants bore the brunt of the crash, with the ‘Magnificent Seven‘ stocks losing nearly $1 trillion in market capitalisation. Nvidia alone saw its valuation drop by $168 billion, while Apple and Amazon lost $162 billion and $72 billion, respectively. The sell-off extended beyond equities, spilling into forex and commodities markets and highlighting the intricate interconnectedness of global financial systems. It underscored the sensitivity of these markets to monetary policy shifts and economic data.
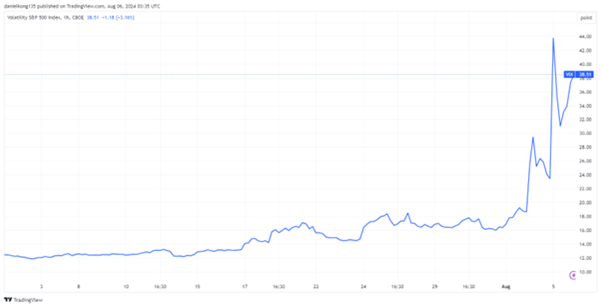
Adding to the turmoil, the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX), a key gauge of market uncertainty, surged dramatically. It rose from around 17 a week earlier to 23 on the preceding Friday and peaked above 65 on Monday morning. By the close of trading, the VIX had moderated to 38.6, marking its highest closing level since the market disruptions of 2020. This sharp spike reflected the heightened market anxiety, reminiscent of the volatility seen during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic.
September Shift: US Implements First Rate Cut Since Recovery [10,11,12,13,14]
In a pivotal shift, the Federal Reserve announced its first interest rate cut since the pandemic recovery, reducing the Federal Funds Rate by 50 basis points to a range of 4.75% to 5.00% during the 18 September 2024 meeting. This marked a departure from the aggressive rate hikes implemented to control inflation, reflecting the Fed’s confidence in the progress made toward stabilising prices and addressing emerging economic challenges. The move followed Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell’s remarks in early August, when he confirmed, “the time has come for policy to adjust,” signaling optimism that inflationary pressures were easing.
The rate cut aimed to stimulate economic growth by reducing borrowing costs, a move initially welcomed by sectors like small-cap stocks, which are particularly sensitive to interest rate changes. However, the stock markets responded with notable volatility. Major indices such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average, S&P 500, and Nasdaq initially experienced a brief surge as investors reacted positively to the prospect of lower borrowing costs and a more accommodative monetary policy.
These gains were short-lived, as concerns over underlying economic weaknesses and uncertainty about the Fed’s long-term policy direction took hold. By the close of trading, the major indices reversed their advances, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average losing 0.25%, the S&P 500 declining by 0.29%, and the Nasdaq Composite dropping 0.31%. The cautious sentiment overshadowed the initial optimism.
The rate cut also had significant repercussions in other markets. Bond yields fell as investors anticipated lower borrowing costs, while the forex market saw a mixed response, with the US Dollar weakening against some currencies amid expectations of reduced rate differentials. The commodities market was also impacted, with gold prices fluctuating as rising Treasury yields and a stronger dollar offset the metal’s safe-haven appeal.
This policy shift highlights the Federal Reserve’s commitment to achieving a “soft landing” for the US economy—balancing efforts to cool inflation while maintaining employment growth. For traders, understanding the ripple effects of this rate cut across various asset classes will be critical to identifying opportunities and managing risks in the evolving economic landscape.
Additionally, with the CPI numbers for November showing steady results, the potential for a December rate cut has strengthened. Headline inflation ticked up to 2.7% annually, while core inflation held steady at 3.3%, aligning with market expectations. These figures reinforce the Fed’s confidence in easing inflationary pressures, despite persistent concerns over economic resilience and labor market conditions.
Markets are now pricing in a near-certain likelihood of another 25 basis point cut in December 2024, reflecting optimism that the Federal Reserve will continue to support growth while carefully managing inflation risks.
November Election Surge: Trump’s Historic Comeback [15]
The 2024 US Presidential Election concluded with Donald Trump achieving a historic victory, becoming the first modern US president to serve non-consecutive terms. His decisive win initially alleviated political uncertainty, providing a boost to financial markets. Major US indices, including the Dow Jones, S&P 500, and Nasdaq, opened at record highs, driven by optimism surrounding Trump’s pro-business policies, such as tax cuts and deregulation.
The Dow surged by 3.6%, adding over 1,500 points, while the S&P 500 and Nasdaq Composite rose by 2.5% and 3%, respectively. This strong market response reflected renewed confidence in industries poised to benefit from Trump’s economic agenda. Key sectors such as energy, defence, and finance experienced notable gains, fueled by expectations of deregulation and increased government spending. Learn more about Trump’s policies and their market implications in our comprehensive article on the “Trump Trade”.
Tesla, under the leadership of Trump supporter Elon Musk, experienced a nearly 15% surge in its stock price. Musk’s outspoken support and active involvement in the campaign fueled expectations that Tesla and his other ventures would thrive under Trump’s pro-business policies, with anticipated regulatory rollbacks poised to reduce competition in the EV market.
Trump’s return to power, coupled with a potential Republican sweep in Congress, is set to shape fiscal and economic policies that will significantly impact market dynamics. Bond yields climbed as concerns over inflation and increased government borrowing pressured bond prices, while the dollar strengthened on expectations of robust economic growth and reduced pressure for immediate Federal Reserve rate cuts.
Gold experienced a sharp sell-off amid rising Treasury yields and a stronger dollar, highlighting the inverse relationship between these assets. However, the longer-term implications of Trump’s policies—such as concern over debt sustainability and potential geopolitical tensions—could renew gold’s appeal as a safe-haven asset in times of economic instability.
Conclusion
The year 2024 has been a transformative period for global markets, driven by significant geopolitical shifts, monetary policy changes, and landmark events. Key developments included Japan’s decision to end negative rates, the Wall Street crash in August, the US rate cut in September, and Trump’s historic presidential comeback in November. These events not only redefined market dynamics but also highlighted the intricate interconnectedness of global financial systems.
For traders and investors, staying informed and understanding the far-reaching impacts of these developments is essential for navigating the complexities of today’s economic landscape and seizing emerging opportunities. As we look ahead to 2025, the focus turns to anticipating new market trends and adapting strategies to thrive in a rapidly evolving environment. Explore our comprehensive 2025 market outlook to stay ahead, and open a live account with Vantage to elevate your trading to the next level.
Reference
- “Japan’s Consolidated Balance Sheet and Challenges for Monetary Policy – Federal Reserve of St Louis”. https://www.stlouisfed.org/on-the-economy/2024/oct/japans-consolidated-balance-sheet-challenges-monetary-policy. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “Bank of Japan raises interest rate to 0.25%, open to further hike this year – Nikkei Asia”. https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Bank-of-Japan/Bank-of-Japan-raises-interest-rate-to-0.25-open-to-further-hike-this-year. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “Markets give off ‘Black Monday’ vibes as stocks tank – Reuters”. https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/global-markets-milestones-graphic-2024-08-05. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “US recession fears send Kospi plunging by record high of nearly 9% – The Korea Herald”. https://koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20240805050583. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “Stock market live updates: Major indexes close sharply lower as investors fear Fed is late to cut rates – NBC News”. https://www.nbcnews.com/business/markets/live-blog/us-stocks-lower-asia-europe-decline-impact-rcna165129. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “$6.4 Trillion Stock Wipeout Has Traders Fearing ‘Great Unwind’ Is Just Starting – Bloomberg”. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-08-05/-6-4-trillion-wipeout-sows-fear-great-unwind-is-just-starting. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “Wall Street’s ‘fear gauge’ — the VIX — hits highest level since the pandemic market plunge in 2020 – CNBC”. https://www.cnbc.com/2024/08/05/wall-streets-fear-gauge-the-vix-rises-to-the-highest-since-2020.html. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “$1 trillion wipeout: Market rout punishes megacap tech – CNBC”. https://www.cnbc.com/2024/08/05/1-trillion-wipeout-market-rout-punishes-mega-cap-tech.html. Accessed 10 December 2024.
- “Stock market recap: Wall Street hammered amid plunging global market – USA Today”. https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2024/08/05/stock-market-dow-jones-nasdaq-live-updates/74671156007/. Accessed 11 December 2024.
- “Fed Chair Powell indicates interest rate cuts ahead: ‘The time has come for policy to adjust’ – CNBC”. https://www.cnbc.com/2024/08/23/fed-chair-powell-indicates-interest-rate-cuts-ahead-the-time-has-come-for-policy-to-adjust.html. Accessed 11 December 2024.
- “The stock market dipped after a historic Fed rate cut. Here’s what the experts think – Fortune”. https://fortune.com/2024/09/18/why-are-stocks-down-rate-cut-fed-interest/. Accessed 11 December 2024.
- “Fed outsized rate cut draws muted reaction, but calm may not last – Reuters”. https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/fed-outsized-rate-cut-draws-muted-reaction-calm-may-not-last-2024-09-19/. Accessed 11 December 2024.
- “What does a Fed rate cut mean for the economy and consumers? – Reuters”. https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/what-does-fed-rate-cut-mean-american-households-2024-09-18/. Accessed 11 December 2024.
- “CPI inflation report sparks Fed interest rate cut bets – Yahoo! Finance”. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/cpi-inflation-report-builds-case-134705958.html. Accessed 12 December 2024.
- “Markets News, November 6, 2024: Stocks Surge to Record Highs After Trump Wins Election; Tesla, Banks, Crypto Among Big Gainers – Investopedia”. https://www.investopedia.com/dow-jones-today-11062024-8740417. Accessed 12 December 2024.



